As plant-based diets become more popular more people are considering making the switch. One of the biggest concerns about this lifestyle change is whether can it provide enough protein. After all, protein is for muscle repair, enzyme production, and overall health. There’s a myth that plant-based diets are low in protein but that’s not true. With a little planning and the right food choices, you can get all the protein you need and enjoy the many benefits of a plant-based diet.
Understanding Protein and Its Role in the Body
What Is Protein and Why Is It Important?
Protein is a macronutrient that is made of amino acids. Amino acids are important for many bodily functions, repair and growth of tissues, the production of enzymes and hormones, and refueling after physical activity. Protein can be found in animal and plant sources and while the amino acid composition may vary the body can use both to meet its needs.
Daily Protein Requirements
The recommended daily consumption of protein varies on age, gender, and your activity level. For most adults, the general guideline is about 46 grams per day for women and 56 grams per day for men. But if you’re an athlete you may need more to support muscle repair and growth. Make sure you’re getting enough protein daily, especially on a plant-based diet.
Common Myths About Protein in Plant-Based Diets
Myth 1: Plant-Based Diets Lack Protein
One of the biggest myths is that plant-based diets don’t have enough protein. But many plant foods are protein-rich – legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. With a variety of these foods in your diet you can easily meet your protein needs without animal products.
Myth 2: You Need Animal Protein for Complete Amino Acids
Another myth is that only animal protein can provide all the essential amino acids, also known as complete proteins. While it’s true that some plant proteins are incomplete, that doesn’t mean they are inadequate. By eating a variety of plant-based foods throughout the day you can easily get all the essential amino acids your body needs. For example, beans with rice or hummus with whole-grain pita can create a complete amino acid profile.
Top Plant-Based Protein Sources
Legumes
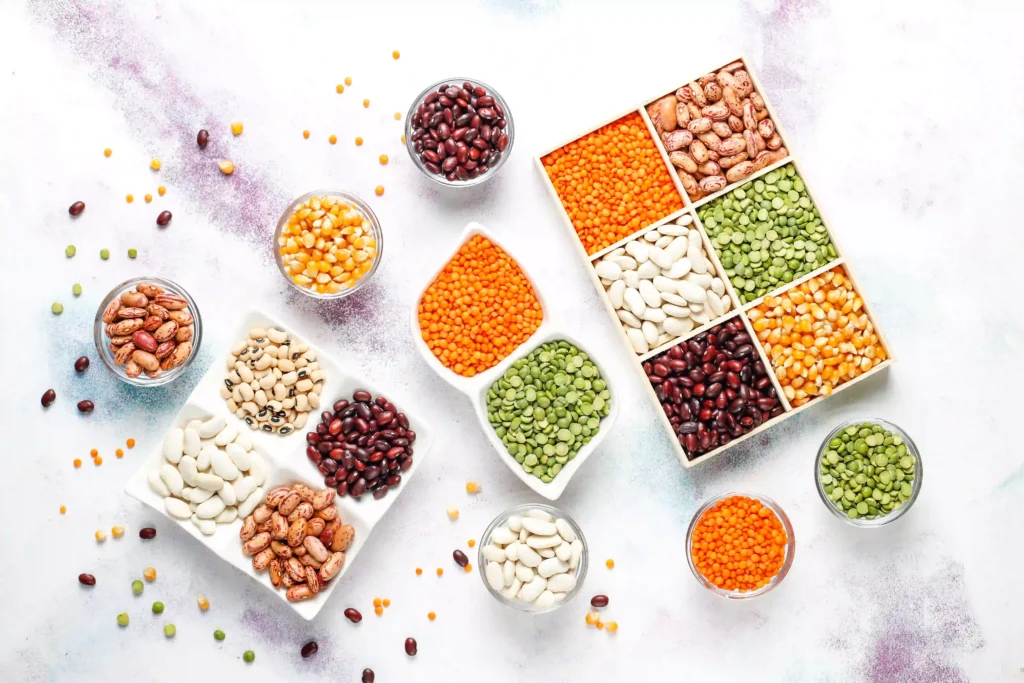

Legumes, including beans, lentils, and peas, are among the best sources of plant-based protein. For example, a cup of cooked lentils contains about 18 grams of protein, making it a fantastic option for meeting your daily requirements. Additionally, legumes are high in fiber, which is beneficial for digestive health. You can add them to soups, stews, and salads, or make them into a delicious plant-based burger.
Nuts and Seeds
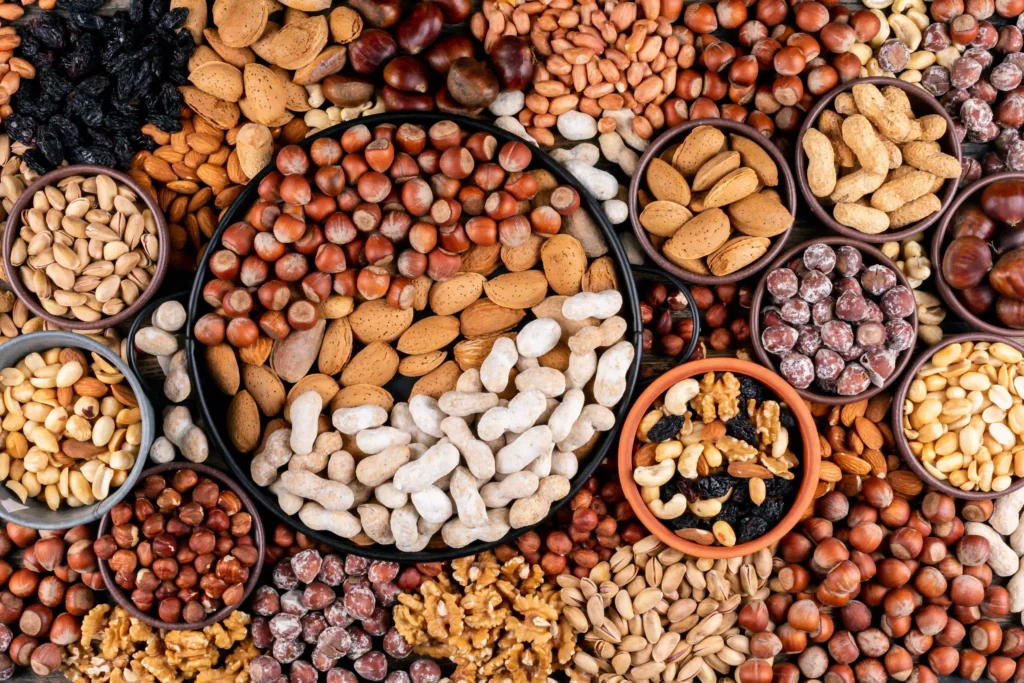

Nuts and seeds like almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are protein powerhouses. For instance, just a quarter cup of almonds provides around 7 grams of protein. These foods are also rich in healthy fats, which are essential for heart health. Nuts and seeds can be sprinkled on oatmeal, blended into smoothies, or eaten as a quick snack to boost your protein intake.
Whole Grains
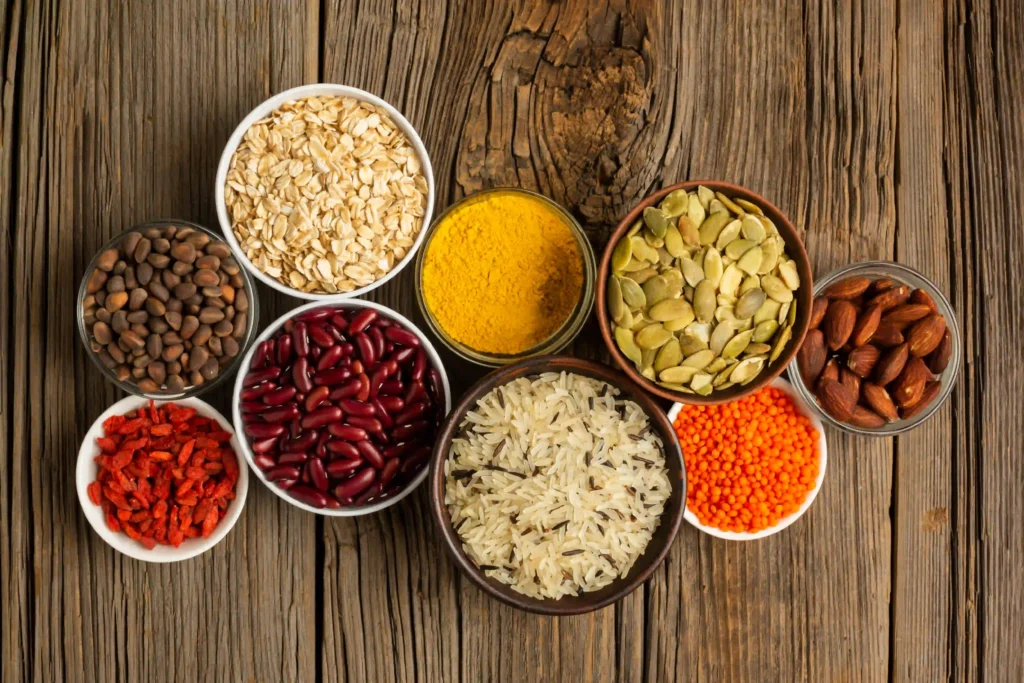

Whole grains such as quinoa, oats, and brown rice are not only rich in carbohydrates but also provide a good amount of protein. Quinoa, for example, contains all nine essential amino acids, that make a complete protein. A single cup of cooked quinoa offers about 8 grams of protein. Incorporating these grains into your meals can help ensure you’re getting a well-rounded nutrient profile.
Tofu, Tempeh, and Edamame
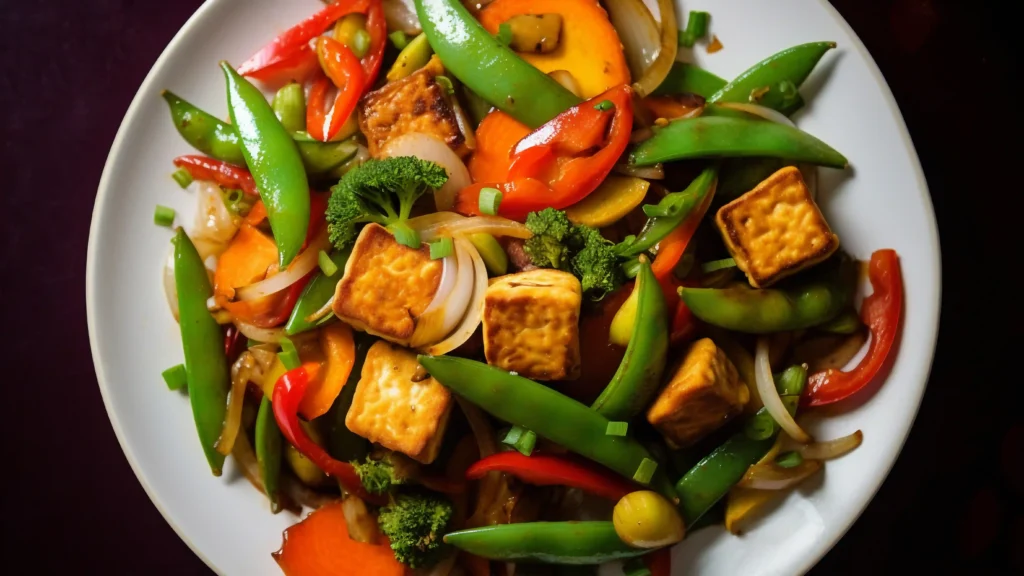
Soy-based products like tofu, tempeh, and edamame are excellent sources of protein. Tofu, made from soybeans, contains about 10 grams of protein per half-cup serving, while tempeh offers even more at approximately 15 grams per half-cup. These versatile foods can be used in a variety of dishes, from stir-fries to salads, and can be seasoned to mimic the flavors of meat.
Vegetables and Leafy Greens
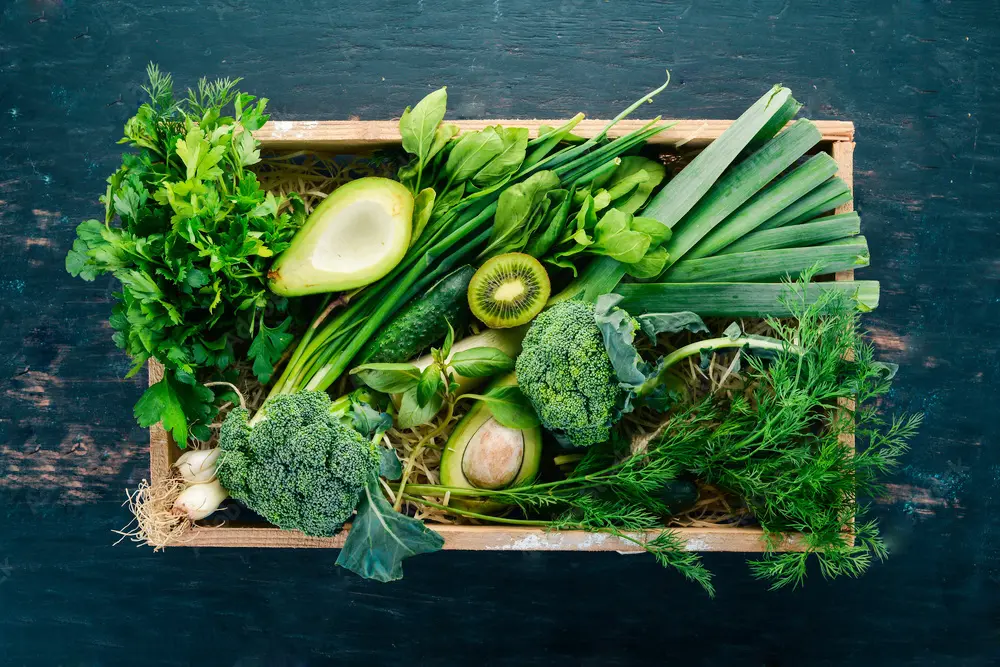

It might surprise you, but vegetables, especially leafy greens, also contribute to your protein intake. Spinach, broccoli, and kale are particularly rich in protein. For example, a cup of cooked spinach provides around 5 grams of protein. While vegetables may not be the primary source of protein, they add valuable nutrients to your diet and help in reaching your daily protein goals.
Plant-Based Protein Powders
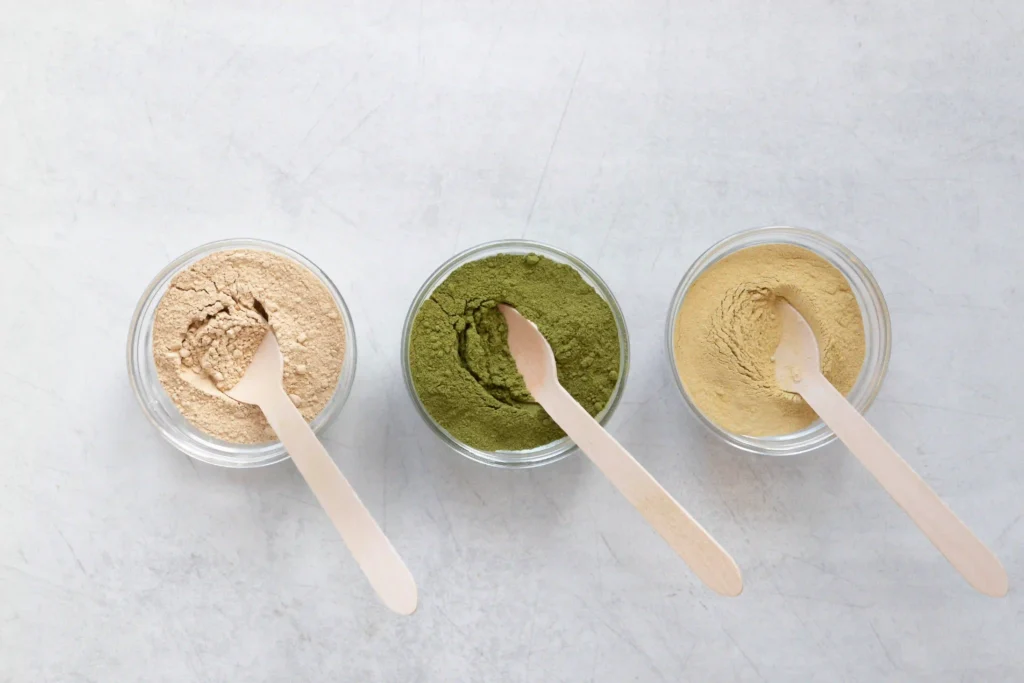

For those is an easy and convenient way to boost your protein intake. There are various plant-based protein powders available, such as pea protein, hemp protein, and rice protein. These powders can be added to smoothies, baked goods, or even sprinkled over oatmeal. While they shouldn’t replace whole foods, they can be a helpful supplement, especially for athletes or those with higher protein needs.
Building a Balanced Plant-Based Diet
Meal Planning for Protein Intake
You need to plan a bit to get enough protein on a plant-based diet but it’s definitely doable. Start by including high protein foods in every meal. For breakfast, you might have oatmeal with chia seeds and almonds. Lunch could be a quinoa salad with beans and veggies and dinner could be a tofu stir fry with brown rice. Snacks like humm from hummus with veggies or a handful of nuts can add to your daily protein intake.
Foods to Combine
To get maximum protein and all essential amino acids you need to combine different plant-based foods. Combining foods like rice and beans, lentils and whole grain bread, or hummus and pita can give you a complete protein profile. By varying your diet and including different protein sources you’ll cover all your bases.
Benefits of a High-Protein Plant-Based Diet
Improved Muscle Health
A plant-based diet rich in protein supports muscle health just as effectively as an animal-based diet. Studies have shown that athletes and bodybuilders can build and maintain muscle mass on a plant-based diet when it’s well-planned. The key is to get enough protein and vary your sources.
Weight Management
Protein is known to promote feelings of fullness, during a meal. A diet rich in plant-based protein can help with weight management by reducing overall calorie intake. Foods like lentils, chickpeas, and tofu are not only filling but also low in calories compared to their animal-based counterparts.
Enhanced Digestive Health
Many plant-based proteins, such as legumes and whole grains, are also high in fiber, which is essential for healthy digestion. A high-fiber diet can help prevent constipation, reduce the risk of certain diseases like colon cancer, and promote a healthy gut microbiome.
Addressing Challenges in a Plant-Based Diet
Ensuring Variety and Avoiding Monotony
One of the challenges of a plant-based diet is the potential for monotony. To keep your diet interesting try new recipes, and different spices and include a wide variety of foods in your meals. The more varied your diet the more possibly you are to get all the nutrients you need.
Nutritional Gaps and How to Fill Them
A plant-based diet can provide all the nutrients but we need to be mindful of certain vitamins and minerals that are less common in plant foods. Vitamin B12, iron, and omega 3s are examples of nutrients that may need to be supplemented or planned for. Fortified foods, supplements and specific plant foods can help fill those gaps.
Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
Starting Small: Tips for Beginners
If you’re new to plant-based eating start by gradually adding more plant-based meals into your diet. You could start with a meatless Monday and then increase the number of plant-based meals you eat each week. This gradual approach allows your body and taste buds to adjust and makes the transition easier.
Overcoming Social and Cultural Barriers
Eating plant-based can be tough in social situations or in certain cultural contexts where meat is a staple. Communicate your dietary preferences with family and friends and find ways to enjoy social gatherings without compromising your diet. Bring a plant-based dish to share or suggest restaurants with plant-based options that can help with these situations.
Maintaining a Balanced Plant-based Diet on a Budget
Plant-based eating can be cost-effective, but it requires some planning. Buying in bulk, focusing on whole foods like legumes and grains, and cooking at home can significantly reduce costs. Additionally, seasonal vegetables and fruits are often more affordable and packed with nutrients.
Conclusion
Including a rich source of protein in a plant-based diet is not only possible but also incredibly beneficial for your health. By understanding your protein needs, debunking common myths, and focusing on diverse and high-quality plant-based protein sources, you can thrive on this diet. The benefits of a plant-based diet from better muscle health to better weight management to better digestion are worth the effort. So whether you’re transitioning to a plant-based diet or looking to optimize your current one, you can get all your nutritional needs including protein from delicious plant-based foods.
FAQs
Q1. Is anything missing from a plant-based diet that includes protein?
While plant-based diets can provide all essential nutrients, it’s important to monitor your intake of vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, as these may be less abundant in plant foods.
Q2. Can I build muscle on a plant-based diet?
Absolutely! With adequate protein intake from a variety of plant-based sources, you can build and maintain muscle mass effectively.
Q3. How do I know if I am getting much protein?
Monitoring your energy levels, muscle mass, and overall health can indicate if you’re getting enough protein. Tracking your food intake using apps or consulting with a nutritionist can also help.
Q4. What are some quick plant-based protein snacks?
Some quick and easy options include a handful of nuts, a protein smoothie with plant-based powder, or hummus with veggies.
Q5. Can children grow on a plant-based, high-protein diet?
Yes, children can grow on a plant-based diet as long as it’s well-planned and includes a variety of protein-rich foods. It’s important to ensure they receive all essential nutrients for their growth and development.


платформа для покупки аккаунтов платформа для покупки аккаунтов
платформа для покупки аккаунтов маркетплейс аккаунтов
купить аккаунт продажа аккаунтов
гарантия при продаже аккаунтов площадка для продажи аккаунтов
продать аккаунт https://prodat-akkaunt-online.ru
безопасная сделка аккаунтов https://kupit-akkaunt-top.ru/
продать аккаунт магазин аккаунтов социальных сетей
Find Accounts for Sale Account Selling Service
Profitable Account Sales Buy Pre-made Account
Verified Accounts for Sale Account marketplace
Account marketplace Buy Account
Sell accounts Marketplace for Ready-Made Accounts
Sell Pre-made Account Accounts market
Account market Account Trading
Marketplace for Ready-Made Accounts Account Market
Social media account marketplace Buy and Sell Accounts
Guaranteed Accounts Account Catalog
account trading service social media account marketplace
account trading service account purchase
secure account purchasing platform account market
buy accounts account sale
buy accounts account store
website for selling accounts marketplace for ready-made accounts
account exchange account trading platform
account buying service gaming account marketplace
account sale account buying platform
account buying service online account store
accounts marketplace account market
account trading service verified accounts for sale
online account store buy accounts
account market account sale
buy and sell accounts https://buy-soc-accounts.org
account acquisition verified accounts for sale
sell accounts account selling service
accounts market social media account marketplace
account catalog website for selling accounts
find accounts for sale account acquisition
gaming account marketplace verified accounts for sale
accounts market ready-made accounts for sale
guaranteed accounts account market
buy account purchase ready-made accounts
account trading guaranteed accounts
accounts for sale account trading platform
ready-made accounts for sale social media account marketplace
purchase ready-made accounts https://accounts-offer.org/
accounts for sale https://accounts-marketplace.xyz/
secure account sales https://social-accounts-marketplaces.live/
find accounts for sale https://accounts-marketplace.live
account trading platform https://social-accounts-marketplace.xyz
guaranteed accounts https://buy-accounts.space/
account buying platform https://buy-accounts-shop.pro/
account store https://buy-accounts.live
buy pre-made account https://accounts-marketplace.online
accounts for sale https://social-accounts-marketplace.live
buy and sell accounts https://accounts-marketplace-best.pro
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей akkaunty-na-prodazhu.pro
маркетплейс аккаунтов rynok-akkauntov.top
биржа аккаунтов https://kupit-akkaunt.xyz/
купить аккаунт купить аккаунт
продать аккаунт магазины аккаунтов
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей магазины аккаунтов
маркетплейс аккаунтов https://akkaunty-optom.live/
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей online-akkaunty-magazin.xyz
маркетплейс аккаунтов купить аккаунт
биржа аккаунтов kupit-akkaunt.online
facebook ad account buy buy facebook account
buying fb accounts buy old facebook account for ads
facebook ads accounts https://buy-ad-account.top
facebook ads account for sale https://buy-ads-account.click
buy account facebook ads ad-account-buy.top
buy facebook ad account https://buy-ads-account.work
cheap facebook account ad-account-for-sale.top
buying facebook account https://buy-ad-account.click
buy facebook old accounts https://ad-accounts-for-sale.work/
buy google adwords accounts https://buy-ads-account.top
adwords account for sale https://buy-ads-accounts.click
facebook ads account for sale facebook ad account buy
google ads reseller https://ads-account-for-sale.top
google ads agency account buy buy google ad account
google ads account for sale https://buy-ads-invoice-account.top
buy google ads account https://buy-account-ads.work
buy aged google ads accounts https://buy-ads-agency-account.top
google ads agency account buy buy verified google ads account
buy facebook bm https://buy-business-manager.org
buy aged google ads account https://buy-verified-ads-account.work
buy verified bm facebook https://buy-bm-account.org/
buy facebook ads accounts and business managers https://buy-verified-business-manager-account.org
facebook bm account buy facebook bm buy
verified bm for sale facebook business manager account buy
unlimited bm facebook business-manager-for-sale.org
buy verified facebook business manager buy-business-manager-verified.org
unlimited bm facebook buy-bm.org
buy verified business manager facebook https://buy-business-manager-accounts.org/
buy tiktok ads https://buy-tiktok-ads-account.org
buy facebook business manager accounts https://verified-business-manager-for-sale.org/
tiktok agency account for sale https://tiktok-ads-account-buy.org
buy tiktok ads https://tiktok-ads-account-for-sale.org
buy tiktok ads https://tiktok-agency-account-for-sale.org
buy tiktok ads https://buy-tiktok-ad-account.org
tiktok ads agency account https://buy-tiktok-ads-accounts.org
tiktok ads account buy https://tiktok-ads-agency-account.org
buy tiktok ads accounts https://buy-tiktok-business-account.org
tiktok ads account for sale https://buy-tiktok-ads.org
This web-based service enables instant conversion of images into JPG format, supporting common types such as JPG. All operations take place within the browser, with no need for app downloads or user accounts. Up to 20 files can be converted in a single session, improving efficiency for repetitive or large-scale tasks. Once files are processed, they are deleted from the system to maintain privacy and prevent unnecessary storage. JPEGtoJPGHERO is designed to work across all devices and browser types, offering a seamless experience whether on a computer, phone, or tablet. Its minimal layout emphasizes clarity and speed, guiding users directly to results. From resizing visuals for websites to preparing files for cloud storage, the platform handles JPEGtoJPGhero conversion with accuracy and ease. Its emphasis on simplicity and security makes it an excellent choice for both casual users and professionals who require consistent, reliable output.
https://vahuk.com/story/jpeg-to-jpg-convert-jpeg-to-jpg-for-free-online/
температура воды в хургаде в апреле
вебкам студия в Варшаве Стань вебкам моделью в польской студии, работающей в Варшаве! Открыты вакансии для девушек в Польше, особенно для тех, кто говорит по-русски. Ищешь способ заработать онлайн в Польше? Предлагаем подработку для девушек в Варшаве с возможностью работы в интернете, даже с проживанием. Рассматриваешь удаленную работу в Польше? Узнай, как стать вебкам моделью и сколько можно заработать. Работа для украинок в Варшаве и высокооплачиваемые возможности для девушек в Польше ждут тебя. Мы предлагаем легальную вебкам работу в Польше, онлайн работа без необходимости знания польского языка. Приглашаем девушек без опыта в Варшаве в нашу вебкам студию с обучением. Возможность заработка в интернете без вложений. Работа моделью онлайн в Польше — это шанс для тебя! Ищешь “praca dla dziewczyn online”, “praca webcam Polska”, “praca modelka online” или “zarabianie przez internet dla kobiet”? Наше “agencja webcam Warszawa” и “webcam studio Polska” предлагают “praca dla mlodych kobiet Warszawa” и “legalna praca online Polska”. Смотри “oferty pracy dla Ukrainek w Polsce” и “praca z domu dla dziewczyn”.
температура воды в хургаде в феврале
хранение резины в паркинге [url=www.shkaf-parking-3.ru/]www.shkaf-parking-3.ru/[/url] .
automotive transport Choosing the Right Car Shipping Company Selecting the best car transport service requires careful consideration. Begin by researching and comparing auto shipping quotes from multiple companies. Pay close attention to the details of each quote, including the types of transport offered (open or enclosed), insurance coverage, and estimated delivery times. Look for companies with a proven track record of reliability and positive customer reviews.
Вова Чернышев
металлопрокат купить в москве цена Металлопрокат в Москве и области: широкий ассортимент и доступность Московский регион предлагает широкий выбор металлопроката от различных производителей и поставщиков. Здесь можно найти стальной прокат (арматуру, балки, швеллеры, листы), трубы, уголки и другие изделия. Доступность различных видов металлопроката позволяет удовлетворить потребности практически любого строительного проекта.
Купить надежный дом под ключ Купить надежный дом под ключ: Мы предлагаем полный комплекс услуг по строительству домов и бань под ключ: от проектирования и подготовки участка до сдачи готового объекта. Обращаясь к нам, вы получаете гарантию качества, соблюдение сроков и фиксированную стоимость.
аккаунт warface Пин-коды Warface: Бонусы и привилегии Пин-коды Warface позволяют получить различные бонусы, такие как VIP-ускорители, кредиты и уникальные предметы. Это отличный способ разнообразить игровой процесс и получить преимущество над противниками.
Группа в Telegram Доска бесплатных объявлений “Все для Вас Архангельск”: товары, услуги, авто, жильё, работа, розыгрыши, отзывы и многое другое. Архангельск, Северодвинск, Новодвинск, Катунино, Березник, Рикасиха, Холмогоры, Мезень, Карпогоры архангельски
Darknet Marketplace Bazaar Drugs Marketplace: A New Darknet Platform with Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace is a new darknet marketplace rapidly gaining popularity among users interested in purchasing pharmaceuticals. Trading is conducted via the Tor Network, ensuring a high level of privacy and data protection. However, what sets this platform apart is its dual access: it is available both through an onion domain and a standard clearnet website, making it more convenient and visible compared to competitors. The marketplace offers a wide range of pharmaceuticals, including amphetamines, ketamine, cannabis, as well as prescription drugs such as alprazolam and diazepam. This variety appeals to both beginners and experienced buyers. All transactions on the platform are carried out using cryptocurrency payments, ensuring anonymity and security. In summary, Bazaar represents a modern darknet marketplace that combines convenience, a broad product selection, and a high level of privacy, making it a notable player in the darknet economy.
научиться кайтсёрфингу Кайт египет
однодневные кайт туры хургада
ремонт стиральных машин в день обращения алматы Комплектующие стиральных машин Алматы. Все необходимое для ремонта и обслуживания.
Бездепозитные бонусы
гибкая керамика phomi цена Гибкая керамика для фасадов дома внутренней отделки Москва phomi купить цена фоми монтаж за 1 м2 отзывы divu
Сукааа казино официальный сайт скачать на андроид мобильная версия бесплатно Sykaaa casino официальный сайт бонус за регистрацию – отличный старт для новых игроков. Получите дополнительные средства для игры сразу после регистрации.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
вавада 100 бесплатных вращений Вавада 100 Бесплатных Вращений: Воспользуйтесь возможностью получить 100 бесплатных вращений в Вавада Казино и увеличьте свои шансы на крупный выигрыш.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
вавада казино официальный рабочее зеркало на сегодняшний день Вавада Казино Официальный Сайт Скачать на Андроид Мобильная Версия Бесплатно: Скачайте мобильную версию Вавада Казино на свое устройство Android и наслаждайтесь игрой в любом месте и в любое время.
амл бот
vavada casino скачать бесплатно на телефон Вавада Казино Официальный Сайт Казино: Погрузитесь в атмосферу азарта и развлечений на официальном сайте Вавада Казино, где вас ждут захватывающие игры и щедрые бонусы.
vavada casino отзывы Vavada Online Casino Официальный Сайт: Посетите официальный сайт Vavada Online Casino и откройте для себя мир азартных игр с высоким качеством и захватывающими возможностями.